Comparative Analysis of South Korea's Real Estate Market: COVID-19 Pandemic vs. 2024
- 공유 링크 만들기
- X
- 이메일
- 기타 앱
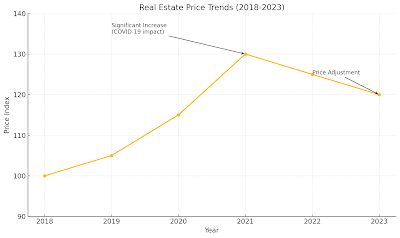
South Korea's real estate market has undergone significant transformations, marked by rapid growth during the COVID-19 pandemic and a shift to a more stabilized environment in 2024. This article provides a detailed comparison of these two periods, focusing on key factors such as interest rates, supply dynamics, investment sentiment, and government policies. The aim is to offer insights for stakeholders to develop informed strategies in the evolving market landscape.
1. Characteristics of the Real Estate Market During the COVID-19 Pandemic (2020–2021)
① Ultra-Low Interest Rates and Increased Borrowing
- Background: In response to the economic impact of the pandemic, the Bank of Korea reduced the base interest rate to a historic low of 0.5%.
- Impact: Lower borrowing costs led to a surge in mortgage applications, fueling housing demand.
- Example: In 2021, Seoul's apartment prices increased by over 20% year-on-year, driven by the low-interest-rate environment.
② Expanded Liquidity and Investment Demand
- Liquidity Injection: The government implemented large-scale fiscal and monetary policies, injecting substantial liquidity into the market.
- Safe-Haven Preference: Amid market volatility, investors viewed real estate as a stable investment alternative.
③ Housing Supply Shortages
- Construction Delays: The pandemic caused delays in construction projects, leading to reduced new housing supply.
- Metropolitan Areas: Chronic supply shortages in Seoul and surrounding regions were exacerbated during this period.
④ Policy Backfires and Psychological Factors
- Government Regulations: Measures such as increased taxes on multiple-property owners and stricter lending rules inadvertently signaled potential price hikes, intensifying buying activity.
- Panic Buying: Fears of being priced out led to a surge in purchases, especially among younger buyers.
⑤ Instability in the Rental Market
- Implementation of the Three Lease Laws: Enacted in 2020, these laws led to a decrease in rental listings and a spike in rental prices.
- Shift to Purchasing: As rental costs rose, many tenants opted to buy homes, further driving up prices.
2. Characteristics of the Real Estate Market in 2024
① High Interest Rates and Borrowing Constraints
- Current Situation: To manage inflation and financial risks, the Bank of Korea has maintained higher interest rates.
- Impact: Increased borrowing costs have dampened buyer enthusiasm, leading to a decline in transactions.
- Outcome: Transaction volumes have decreased, and some regions have experienced price adjustments.
② Reduced Liquidity and Market Stabilization
- Tightened Environment: The large-scale liquidity injections of the pandemic era have been withdrawn, leading to a more stable market.
- Weakened Investment Sentiment: Real estate has become less attractive to investors, resulting in decreased speculative activity.
③ Persistent Supply Shortages
- Efforts to Increase Supply: The government has been working to expand housing supply, but shortages remain acute in high-demand areas like Seoul.
- Long-Term Effects: While new supply may not have immediate impact, it is expected to contribute to market stabilization over time.
④ Prevailing Market Caution
- Shift in Buyer Sentiment: High interest rates and economic uncertainties have led many potential buyers to adopt a wait-and-see approach.
- Potential for Recovery: If interest rates decrease or regulations are eased, buyer sentiment may improve.
3. Strategies for Market Participants
① For Homebuyers
- Monitor Interest Rates: Stay informed about potential rate cuts or stabilization to time purchases effectively.
- Regional Analysis: Focus on areas with strong growth potential, such as regions with upcoming transportation projects or urban redevelopment plans.
② For Investors
- Invest in Development Areas: Target regions undergoing significant infrastructure development or urban renewal for long-term gains.
- Diversify to Mitigate Risks: Invest in areas with strong rental demand to minimize vacancy risks and diversify portfolios.
③ Stay Informed on Market Trends
- Government Policies: Keep abreast of changes in lending regulations, tax incentives, and supply expansion initiatives.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Analyze regional supply and demand balances to make informed investment decisions.
4. Conclusion: Potential for Market Resurgence
The rapid price increases during the COVID-19 pandemic were driven by unique factors such as ultra-low interest rates, large-scale liquidity injections, and supply shortages. In 2024, the market operates under high interest rates and a tightened liquidity environment, making a similar surge less likely. However, localized price increases may occur in key metropolitan areas and regions with significant development projects.
Advice for the Future: Whether for personal residence or investment, it is crucial to analyze the current market environment thoroughly and develop strategies aligned with individual objectives.
References
- Bank of Korea Economic Statistics System
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport
- KB Real Estate Liiv ON
- Statistics Korea
- 공유 링크 만들기
- X
- 이메일
- 기타 앱